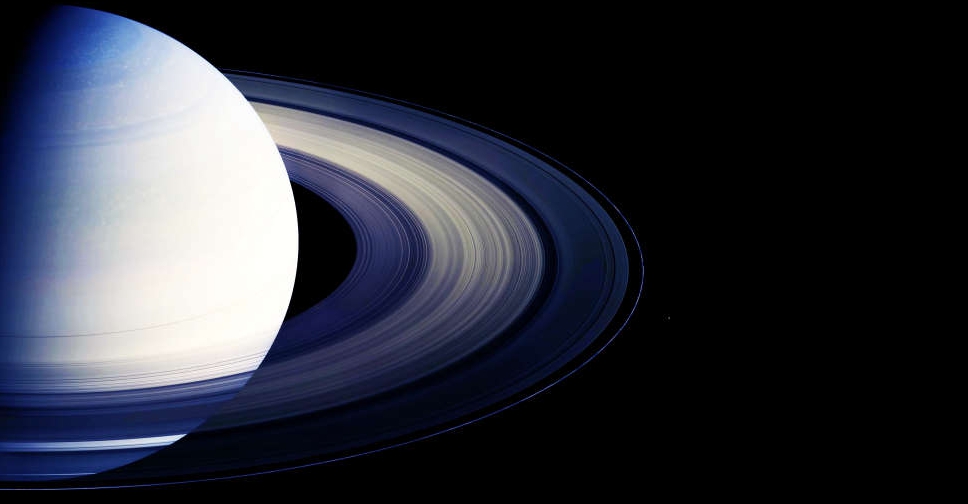
Phosphorus, a crucial chemical component for life, has been discovered on Saturn's moon Enceladus, according to findings published in the journal Nature.
Scientists analysed data from NASA's Cassini mission, which explored Saturn and its moons from 2004 to 2017.
The mission detected phosphorus in salty ice grains released by plumes erupting from cracks in Enceladus' icy surface. Enceladus is known to harbour an ocean beneath its icy shell, and the plumes of material released from its geysers contain minerals and organic compounds necessary for life.
The presence of phosphorus is significant because it is essential for DNA, RNA, cell membranes and energy transport in cells. It is the first time phosphorus has been found in an ocean beyond Earth. The discovery suggests that Enceladus' ocean could potentially support life if it exists on the moon. The study's lead author, Dr. Frank Postberg, emphasised the importance of phosphates, stating that life as we know it would not exist without them.
The research also revealed high concentrations of sodium phosphates in Enceladus' ice grains. These phosphates were dissolved in the moon's ocean water, indicating that they are readily available for the formation of potential life. The study's co-author, Dr. Fabian Klenner, noted that the high phosphate concentrations satisfy one of the crucial requirements for determining the habitability of celestial bodies.
Enceladus' ocean, although located beneath an ice shell, exhibits hydrothermal environments along its seafloor, which help maintain a warmer temperature. The researchers conducted lab experiments to simulate the moon's salty ocean and found that the phosphate concentrations were significantly higher than those in Earth's oceans. The unique characteristics of Enceladus, such as its "soda ocean" rich in carbonates and carbon dioxide, enable the dissolution of large amounts of phosphates.
While Enceladus shows promise for habitability, no actual life has been detected yet.
The next step, according to the study's co-author Dr. Nozair Khawaja, is to return to Enceladus and investigate whether its habitable ocean is inhabited. Astronomers are prioritising the development of the Enceladus Orbilander, a mission that would orbit the moon and land on its surface.
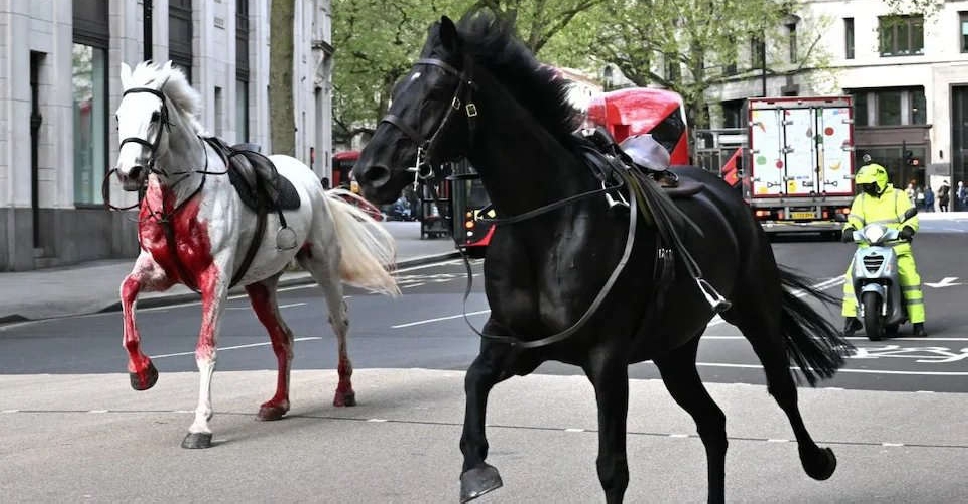
 Horses run amok in central London
Horses run amok in central London
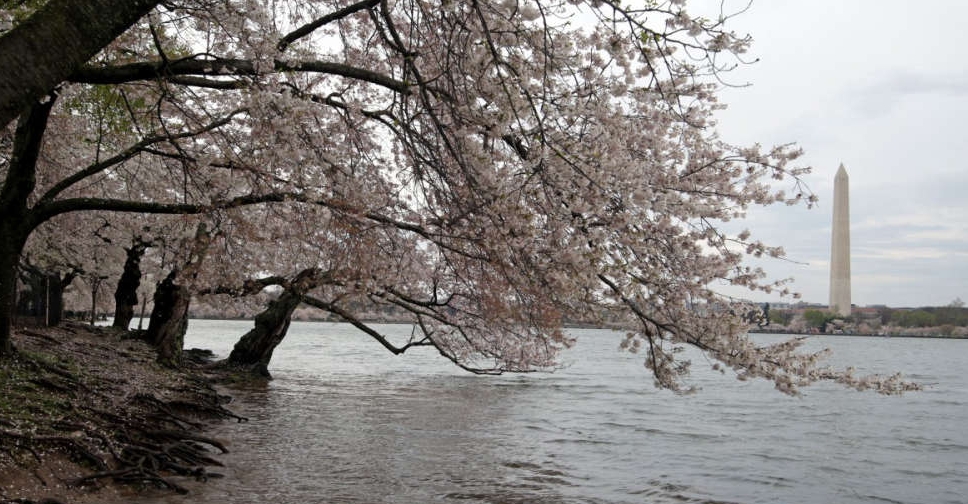 Kishida delights Washington with promise of 250 cherry trees as gift
Kishida delights Washington with promise of 250 cherry trees as gift
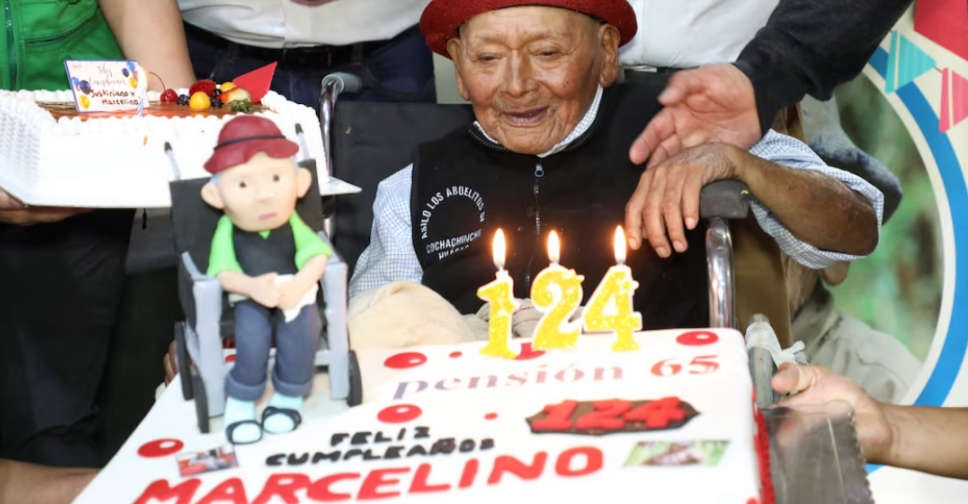 124 candles? Peru stakes claim to world's oldest human, born in 1900
124 candles? Peru stakes claim to world's oldest human, born in 1900
 Germany's Scholz joins TikTok in bid to reach young voters
Germany's Scholz joins TikTok in bid to reach young voters
 'Adopt a penguin egg' Easter campaign helps endangered African birds
'Adopt a penguin egg' Easter campaign helps endangered African birds